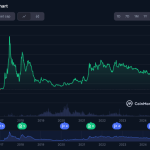
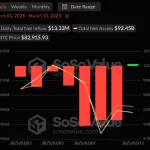
With Bitcoin’s inception in 2009, Satoshi Nakamoto likely never anticipated the digital collectible craze involving CryptoKitties, Punks, Hashmasks, celebrity music, and more.
These utilize Ethereum’s ERC-721 standard, crucial for creating and transferring non-fungible tokens.
This article answers key questions about non-fungible tokens:
What is a non-fungible token (NFT)?
An NFT is a cryptographic token uniquely defining an asset. It can represent digital assets like images or track real-world items like houses, cars, or songs. This uniqueness allows proof of ownership and authenticity.
The need for non-fungible tokens arises from the limitations of ERC-20 tokens, which are divisible and interchangeable.
Non-fungible tokens solve the interchangeability issue, ensuring each token represents a distinct asset.
For instance, fungibility is crucial for digital currencies like Bitcoin, allowing easy trade. In contrast, non-fungible tokens uniquely identify assets.
What are the Characteristics of Non-Fungible Tokens?
Non-fungibility is vital for NFTs, which are valued for their uniqueness, rarity, and indivisibility.
Uniqueness
NFTs uniquely define assets through metadata, differentiating them from others. Projects like Decentraland use metadata to specify virtual land.
Rarity
Rarity ensures NFTs can’t be infinitely duplicated, adding value for collectors.
Indivisibility
NFTs can’t be divided, unlike Bitcoin, which can be split into smaller denominations.
How do Non-Fungible Tokens work?
Ethereum’s ERC-721 standard defines unique assets, finalized in January 2018. It requires metadata, including a URI pointing to a JSON file describing the NFT’s properties.
Why do we need non-fungible tokens?
NFTs are valuable in digital economies, like gaming, where they ensure asset control and trade. Decentralized identity also benefits from NFTs, linking physical properties to identities.
Possible NFT representations include:
-
- Collectibles
-
- Art: both physical and digital
-
- In-game items, such as skins or stickers
-
- Virtual world items, like land
-
- Real-world assets, such as cars or houses
-
- Identity-related properties, such as certifications or medical history.
Here are five notable NFT projects:
Which projects are actively using NFTs?
Numerous projects leverage NFTs, including:
CryptoKitties
CryptoKitties was the first mainstream NFT use, akin to Pokemon Go. It involves collecting and breeding digital cats with unique traits.
Decentraland
Decentraland is a virtual reality world where users own virtual land, develop it, and trade it with others.
Gods Unchained
Gods Unchained is a collectible card game using NFTs to authenticate and trade cards, addressing issues like authenticity and ownership.
NBA Top Shots
NBA Top Shots, on the FLOW blockchain, captures NBA game moments as NFTs with varying rarity, attracting significant interest and investment.
OpenSea Marketplace for NFTs
The OpenSea marketplace allows decentralized NFT trading, hosting over 200 types of NFTs like CryptoKitties and Ethereum domain names.
How to Buy NFTs?
Now, let’s explore NFT purchasing. Popular marketplaces like OpenSea and Rarible require an ERC-721 compatible wallet like MetaMask.
The browsing section of the platform shows trending collections. Below each NFT, you can see the auction time remaining. For this example, we’ll click on the first available NFT – the Wrapped MoonCat.
This is how the specific NFT buying page looks like. You have all the information needed in front of you. This includes the price history (if there’s any trading data), the creator, a description of the NFT, as well as the current offers down below. From here, there are two options.
First, you can buy the NFT directly for its listing price. In this case, it’s 0,9999 ETH. If you want to participate in the auction, however, you need to “make an offer” using the button down below. If your offer is accepted, your account will be debited, and you will receive the NFT in return for the ETH.
NFTs and Beyond
So, how did NFTs manage to receive value? It’s the same as asking why a particular painting is valued at 1,000 euros. Why would you pay $1,000 for a physical painting that may as well be counterfeit as you can own a digital painting of which you know you are the sole owner, and you can prove its authenticity.
..In the end, the value of an NFT depends on how much money one is willing to pay for it, just as with any collectible item. The value isn’t inherent to the object itself but is rather assigned by people who deem it valuable. In essence, value is a shared belief.
It’s also interesting to note that some particular NFTs have absolutely exploded in value. For instance, Beeple’s “The First 5,000 Days” NFT sold for a whopping $69 million.
In conclusion, NFTs have gained a lot of popularity and exposure over recent years as they act as proof of ownership and authenticity of both digital and physical items. On top of that, NFTs allow users to trustlessly transfer ownership, eliminating fraud.